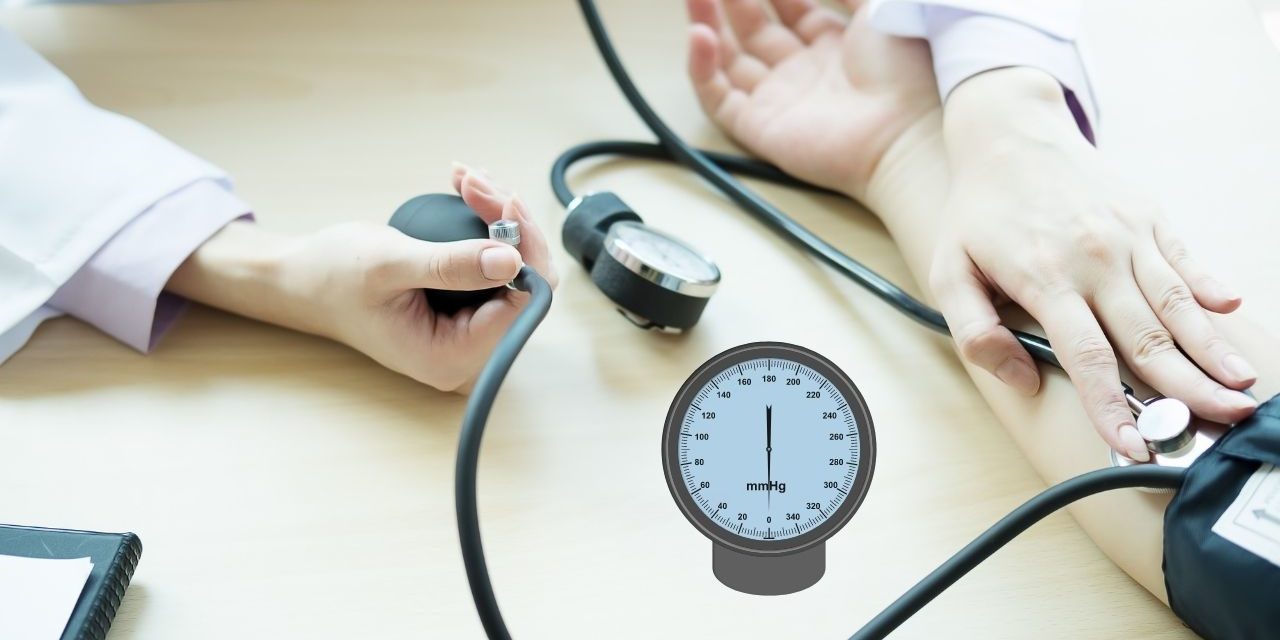
High blood pressure, or high blood pressure, can have a variety of causes, and is often caused by a combination of factors. Understanding the causes of high blood pressure is critical to its prevention, management, and treatment. Here are some important factors that contribute to high blood pressure:
1. Lifestyle factors:
Unhealthy diet: A diet high in sodium (salt) and low in potassium can lead to high blood pressure. Excess sodium can cause fluid retention and increase blood volume, while potassium helps control blood pressure.
•Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of regular physical activity and sedentary lifestyle can lead to high blood pressure. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, strengthen the cardiovascular system, and improve blood flow.Excessive alcohol consumption: Drinking large amounts of alcohol can increase blood pressure. Regular and excessive alcohol consumption can also lead to other health problems, such as liver disease, which can further increase high blood pressure.
2. Obesity:
Being overweight or obese increases the risk of high blood pressure. Being overweight puts extra stress on the heart, increases blood volume, and contributes to insulin resistance, which can lead to high blood pressure.
3. Genetics and Family History:
Family history plays a role in high blood pressure. If your parents or close relatives have high blood pressure, you may be at higher risk of developing it. Genetic factors can affect how the body regulates blood pressure.
4. Age:
Blood pressure increases with age. This is partly due to the natural process of aging, as blood vessels become less flexible and stiffer over time.
5. Ethnicity:
Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, are at increased risk of developing high blood pressure. They tend to develop high blood pressure at a younger age and have more severe complications.
6. Chronic Conditions and Medical Factors:
• Chronic kidney disease:
Impaired kidney function can lead to fluid and sodium retention, which in turn increases blood pressure.
Diabetes:
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are associated with an increased risk of high blood pressure. High blood sugar levels and insulin resistance can damage blood vessels and affect blood pressure regulation.
Hormonal conditions:
Conditions such as thyroid disorders (hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism) and Cushing’s syndrome can contribute to high blood pressure.
• Sleep apnea:
Obstructive sleep apnea, a sleep disorder characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, is associated with high blood pressure. Repeated episodes of oxygen deprivation can raise blood pressure levels.
7. Medicines and Supplements:
Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), decongestants, hormonal contraceptives, and some antidepressants, can raise blood pressure. Additionally, heavy use of over-the-counter supplements such as weight loss products and certain herbal remedies can also contribute to high blood pressure.
It is important to note that in many cases, the exact cause of high blood pressure may not be identifiable. This is known as essential or primary high blood pressure, which is the most common type. Managing high blood pressure usually involves a combination of lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, weight management, stress reduction, and, if necessary, health care. Medicines prescribed by a professional. It is always recommended to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis of high blood pressure and a personalized treatment plan.