Introduction:
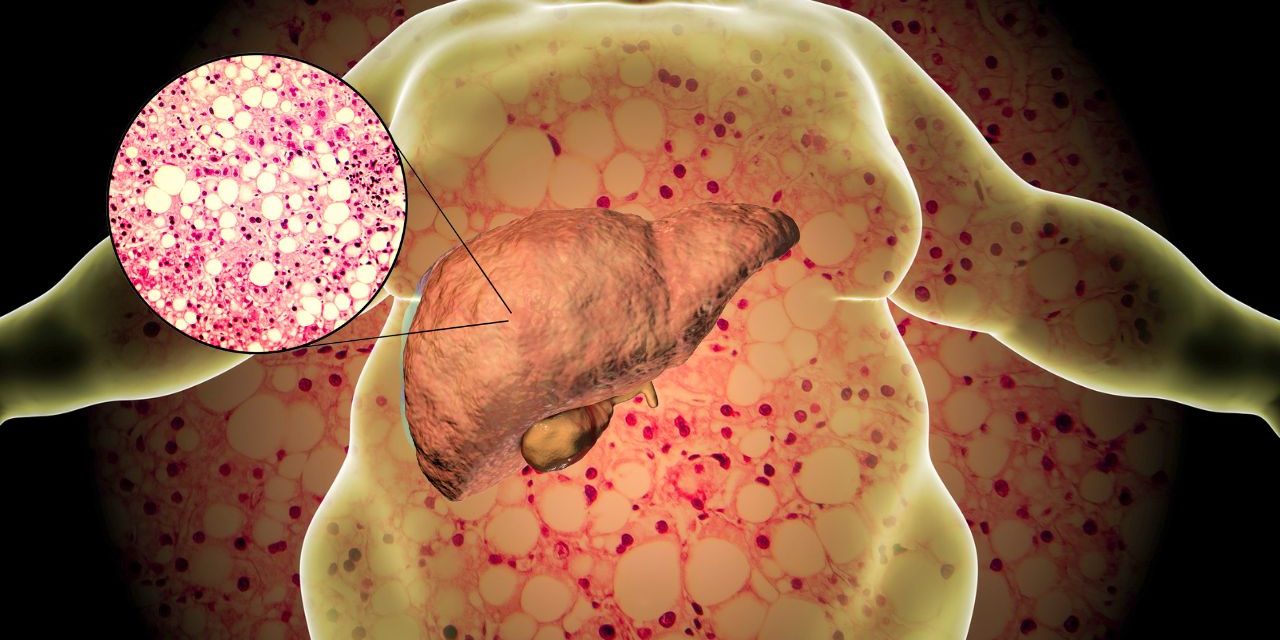
Hepatomegaly, commonly known as an enlarged liver, is a medical condition characterized by an increase in liver size beyond its normal range. It can be the result of various underlying health problems, from benign conditions to severe liver diseases. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the possible causes of hepatomegaly are critical for early detection and appropriate management. In this comprehensive article, we explore the world of hepatomegaly, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options to promote liver health and overall wellness.
Definition of Hepatomegaly:
The liver is an important organ responsible for a number of essential functions, including filtering toxins, metabolizing nutrients, and producing bile for digestion. Hepatomegaly occurs when the liver becomes abnormally large, expanding beyond its normal size. This enlargement can be mild, moderate or severe depending on the underlying cause.
Common causes of hepatomegaly:
Liver infections: Viral hepatitis (such as hepatitis A, B, C, or E), infectious mononucleosis, and other viral or bacterial infections can cause hepatomegaly.
Liver diseases: Conditions such as fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, liver cysts, or liver tumors can cause liver enlargement.
Alcohol abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption over time can lead to alcoholic liver disease, which leads to hepatomegaly.
Metabolic disorders: Certain genetic or metabolic disorders, such as Wilson’s disease or hemochromatosis, can cause liver enlargement.
Heart failure: Severe heart conditions can cause blood to back up in the liver, resulting in hepatomegaly.
Side effects of medications: Some medications can cause liver enlargement as a side effect.
Recognize the symptoms:
In many cases, hepatomegaly may not present with significant symptoms. When symptoms appear, they may include:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Fatigue or weakness.
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Swelling in the abdomen or legs
- Unintentional weight loss
Diagnostic Methods:
If hepatomegaly is suspected, a health care professional may use a variety of diagnostic methods, including:
Physical examination: The doctor may palpate the abdomen to feel for an enlarged liver and look for other physical signs of liver disease.
Blood tests: Liver function tests and other blood tests can provide insight into liver health and possible causes of hepatomegaly.
Imaging studies: Ultrasonography, CT scan, or MRI may be used to visualize the size of the liver and identify structural abnormalities.
Biopsy: In some cases, a liver biopsy may be performed to obtain a small sample of liver tissue for further analysis.
Management and Treatment:
Treatment of hepatomegaly depends on its underlying cause. Some general steps to promote liver health include:
Lifestyle changes: Adopting a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can benefit liver health.
Medication: Specific medications may be prescribed to treat infections, manage liver diseases, or deal with metabolic disorders.
Interventional procedures: In some cases, procedures such as removing fluid from the abdomen or removing a liver tumor may be necessary.
Liver Transplant: In liver failure or end-stage liver disease, liver transplantation may be the only survival option.
Result:
Hepatomegaly, or an enlarged liver, can be caused by a wide range of conditions, from benign to severe liver diseases. Early diagnosis and accurate diagnosis are crucial for timely intervention and effective management. By recognizing the potential symptoms and risk factors of hepatomegaly and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can take steps to promote liver health and overall health. Since the liver plays an important role in maintaining various bodily functions, it is important to prioritize liver health through a balanced lifestyle and regular medical check-ups.