Introduction:
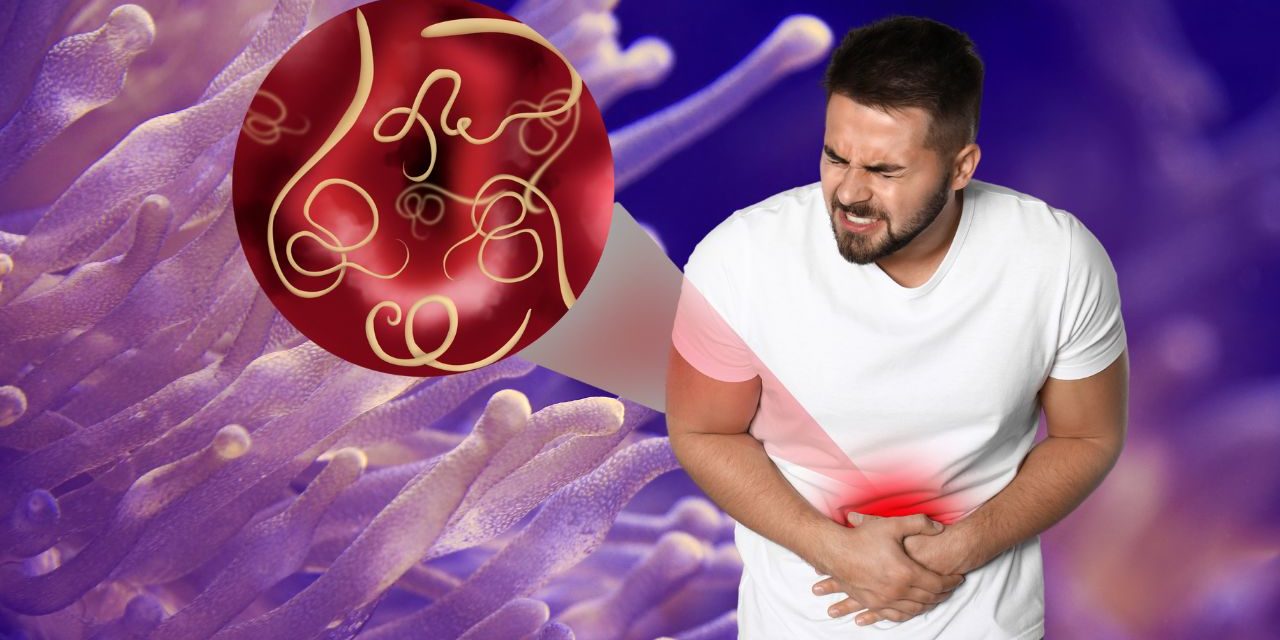
Intestinal worms, also known as intestinal parasites, are a common health concern that affects millions of people worldwide, especially in regions with poor sanitation and hygiene. These parasitic organisms live in the gastrointestinal tract and can cause symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe health complications. Understanding the different types of intestinal worms, recognizing their symptoms, and implementing effective preventative measures and treatments are essential steps to maintaining optimal intestinal health. In this comprehensive article, we explore the world of intestinal worms, highlighting their types, symptoms, treatment options, and preventative measures.
Types of Intestinal Worms:
There are several types of intestinal worms that can infect humans, including:
Roundworm (Ascaris lumbricoides): The most common type of intestinal worm worldwide, roundworms can be several inches long and can cause abdominal pain, coughing, and indigestion.
Hookworms (Ancylostoma duodenale, Necator americanus): Hookworms attach to the intestinal lining and feed on blood, causing anemia, fatigue, and abdominal pain.
Whipworms (Trichuris trichiura): These worms live in the large intestine and can cause diarrhea, abdominal pain and weight loss.
Tapeworms (Taenia spp): Tapeworms can be infected by eating undercooked or raw meat, and can cause mild symptoms or more severe complications.
Pinworms (Enterobius vermicularis): Commonly found in children, pinworms cause severe itching around the anus and can disturb sleep.
Recognizing the symptoms of an intestinal worm infection:
Symptoms of an intestinal worm infection can vary depending on the type of worm and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Itching around the anus (common in pinworm infections)
- Worms seen in stool (rare)
Treating Intestinal Worms:
Treatment for intestinal worm infections usually includes antiparasitic medications prescribed by a healthcare professional. The specific medication and duration of treatment depends on the type of worm and the severity of the infection. It is important to follow the recommended treatment regimen and consult a healthcare provider before taking any over-the-counter treatment.
Precautions:
Preventing intestinal worm infections requires adopting several hygiene and lifestyle practices, including:
Hand hygiene: Regular hand washing with soap and clean water, especially before eating or after using the bathroom, is very important to prevent insect infestation.
Proper food preparation: Ensuring that meat is well cooked and maintaining proper food hygiene can prevent tapeworm infection.
Avoiding contaminated water: Drinking clean, treated water can help prevent the release of parasite eggs.
Shoes: Wearing shoes in areas with poor sanitation can prevent hookworm infection through the skin.
Personal and household hygiene: Keeping living spaces clean, washing bedding regularly, and avoiding sharing personal items can reduce the risk of transmission of worms.
Result:
Intestinal worm infections remain a major global health concern, particularly in areas with inadequate sanitation and hygiene practices. Understanding the different types of intestinal worms, recognizing their symptoms, and implementing preventative measures are critical to maintaining optimal intestinal health. Timely medical treatment should be sought in case of infection to prevent complications and further transmission. By promoting good hygiene practices, proper food handling, and access to clean water, we can work to reduce the burden of intestinal worm infections and ensure healthier communities around the world.