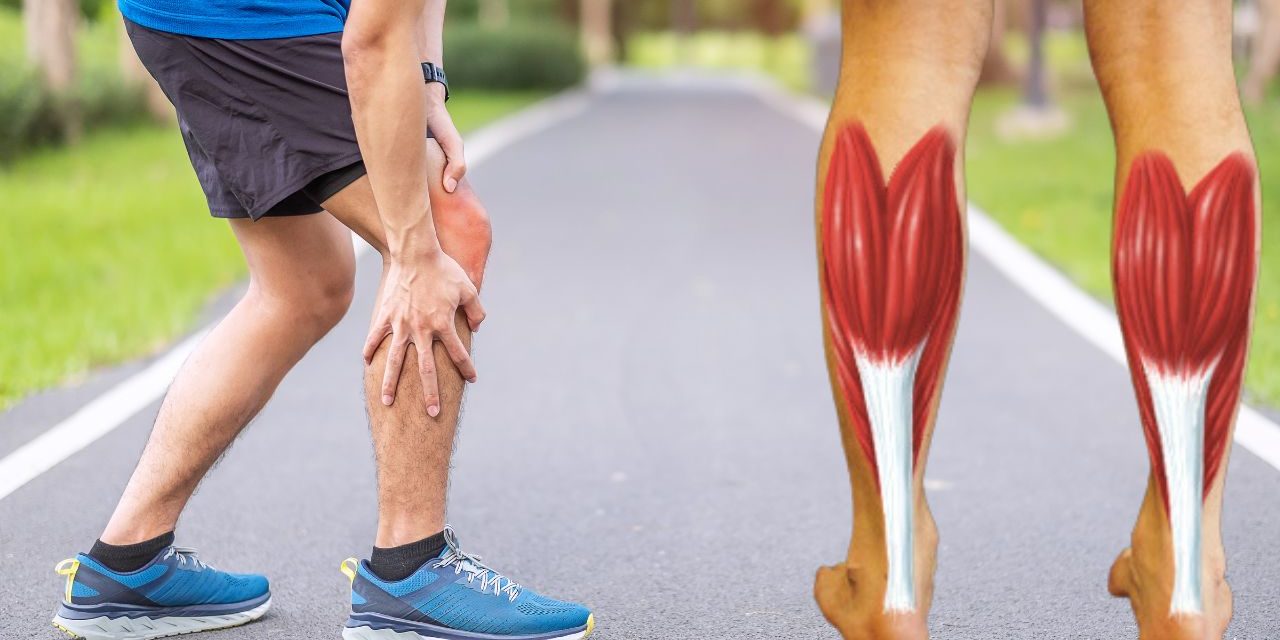
Introduction
Tendonitis, also known as tendonitis, is a common condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of the tendon. Tendons are tough, fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones and play an important role in joint movement. Tendinitis can affect people of all ages and is often caused by overuse or repetitive motions that stress the tendon. It usually occurs in areas such as the shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, knees and ankles. Understanding the nature of tendinitis, its possible causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential to promote early diagnosis and effective management. In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore tendinitis, its underlying causes, common symptoms, and the most appropriate treatment methods to help people find relief and promote tendon healing.
Nature of Tendinitis
Tendonitis occurs when a tendon becomes inflamed or irritated due to repetitive motion, overuse, or injury. This causes pain, tenderness, and limited movement in the affected area. Tendinitis can affect different tendons in the body, depending on the activities and movements involved.
Possible Causes of Tendinitis
Tendinitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Repeated use: Repeatedly performing the same movement or activity, such as in sports or work-related tasks, can stress tendons.
- Age: As people age, tendons can become less flexible and more prone to injury.
- Improper technique: Using improper form or technique during physical activity can increase the risk of tendinitis.
- Muscle imbalance: Muscle imbalance or weakness can put too much stress on the tendon.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes, can increase the risk of tendinitis.
Symptoms of Tendinitis
Tendinitis presents with specific symptoms, including:
- Pain: Pain is the primary symptom, which can range from mild to severe.
- Swelling: The affected area may be swollen and tender to touch.
- Stiffness: Limited joint mobility and stiffness may be experienced.
- Warmth: In some cases, the affected area may feel warm to the touch due to inflammation.
Effective treatment methods
Treatment for tendinitis focuses on reducing inflammation, relieving pain, and promoting tendon healing. Common methods include:
- Rest: Giving the affected tendon time to heal through less activity and rest.
- Ice and compression: Applying ice packs and compression bandages can help reduce swelling.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers can provide temporary relief from discomfort.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can create an appropriate exercise program to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and promote tendon healing.
- Corticosteroid injection: In severe cases, a doctor may administer a corticosteroid injection to reduce swelling.
- Extracorporeal Shack Wave Therapy (ESWT): ESWT can be used to accelerate tendon healing in resistant cases.
Precautions
Prevention of tendonitis involves taking proactive steps, such as:
- Gradual progression: gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activities to avoid sudden stress on the tendons.
- Proper Technique: Using proper form and technique during sports or exercise.
- Proper warm-up: Engaging in warm-up exercises before physical activity to prepare muscles and tendons.
- Rest and recovery: allowing enough time for rest and recovery between physical activities.
When to seek medical attention
Although most cases of tendinitis respond well to conservative measures, individuals should seek medical attention if:
- Pain and swelling worsen: Symptoms become more severe despite rest and home care.
- Limited mobility: Tendinitis is affecting daily activities and joint function.
- Recurrent Tendinitis: Tendinitis tends to recur despite adequate rest and prevention strategies.
Result
Tendinitis is a common condition that can cause pain, swelling, and limited joint movement. Understanding the possible causes, symptoms, and available treatment options empowers individuals to effectively manage and alleviate tendinitis. Most cases of tendinitis can be treated with rest, home care, and physical therapy. However, seeking medical evaluation for acute or recurrent tendinitis is critical to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. With the right approach and support, individuals can recover from tendonitis, promote tendon healing, and resume their regular activities with improved joint health and overall health.