Introduction
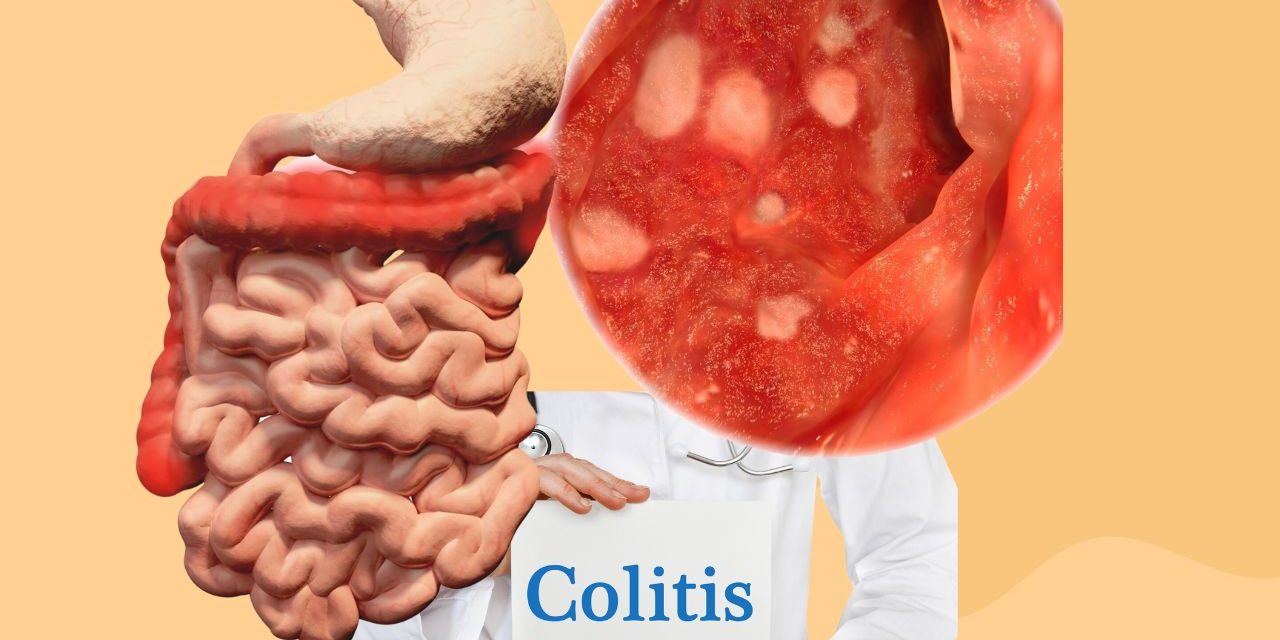
Colitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the colon, which can cause a number of uncomfortable symptoms and affect a person’s quality of life. Although there are different types of colitis, the most common forms are ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, both of which are chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. In this article, we will review the symptoms of colitis, its possible causes, and the various treatment options available to effectively manage the condition.
Understanding Colitis: Types and Causes
Colitis refers to inflammation of the large intestine, also known as colon. There are different types of colitis:
- Ulcerative colitis: A chronic inflammatory bowel disease that affects the inner lining of the large intestine and rectum.
- Crohn’s disease: Another chronic inflammatory bowel disease that can affect any part of the digestive system, from the mouth to the anus, with the most common sites being the end of the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine.
- Microscopic colitis: A type of colitis that can only be seen under a microscope during a biopsy.
The exact cause of colitis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be the result of a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors that trigger an abnormal immune response, leading to inflammation.
Recognizing the symptoms of colitis
- Symptoms of colitis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition.
- Stomach aches and pains
- Diarrhea (which can be bloody in ulcerative colitis)
- Bleeding from the rectum
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- fever
- Dehydration
Assessment and diagnosis
If colitis is suspected, a gastroenterologist will perform a thorough evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical exam, blood tests, stool tests, and imaging studies (such as colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy) to confirm the diagnosis. and extent of inflammation can be determined.
Treatment options for colitis
Treatment for colitis is aimed at managing symptoms, achieving remission, and preventing complications. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications, immunosuppressants, and biologics are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response.
- Lifestyle changes: Dietary changes, stress management, and regular exercise can help improve overall health and reduce symptoms.
- Dietary treatment: In some cases, a special diet or nutritional supplements may be recommended to promote healing and reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: In severe cases of colitis that do not respond to other treatments or if there are complications, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected part of the colon.
Managing flare-ups and remissions
Colitis is often characterized by intermittent flare-ups and remissions. During a flare-up, symptoms may worsen, while remission refers to a period of lack or disappearance of symptoms. Working closely with a health care provider is critical to managing these steps effectively.
Result
Colitis is a complex and chronic condition that can significantly affect a person’s daily life. Early diagnosis, regular medical follow-up, and appropriate treatment are essential to manage symptoms, achieve remission, and prevent complications. By being aware of their condition, making necessary lifestyle adjustments, and following recommended treatments, people with colitis can take control of their condition and improve their overall health. Gaining support from health care professionals, family, and friends can also play an important role in coping with the challenges posed by colitis and maintaining a positive outlook on the journey of overcoming this inflammatory bowel disease. can do.