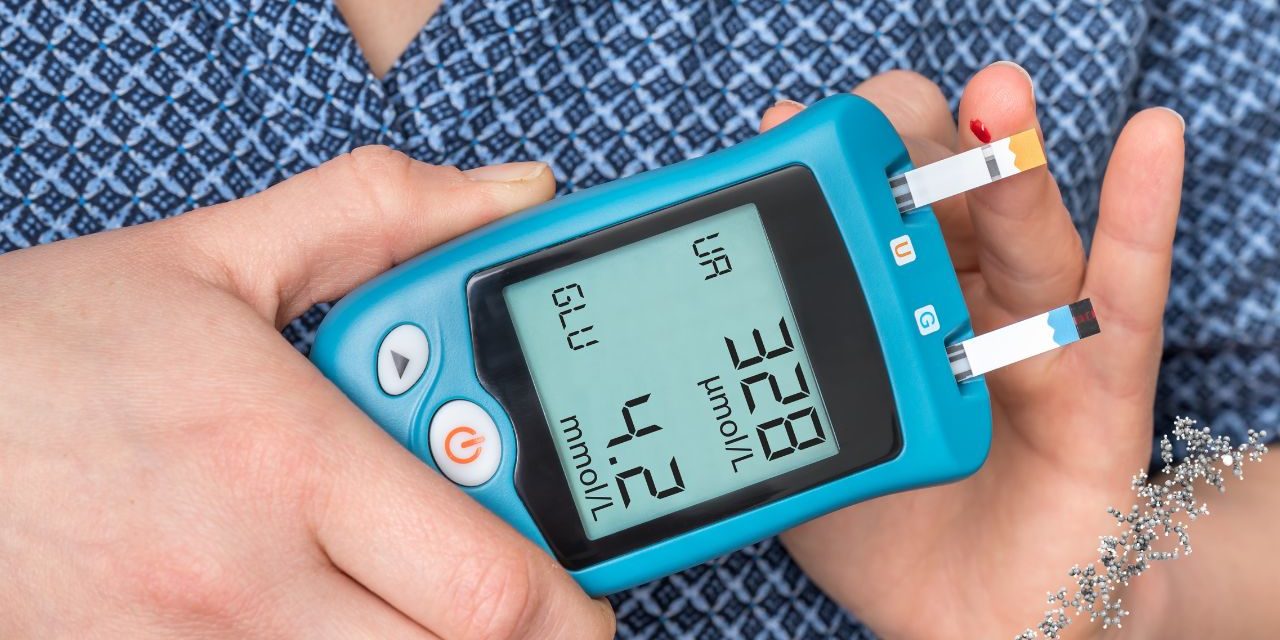
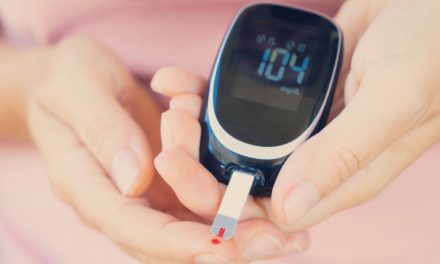
- Normal blood sugar levels refer to the amount of glucose (sugar) present in your bloodstream. Glucose is a type of sugar that is given to the primary source of energy for your body cells. It comes from the food we eat and is regulated by the hormone insulin in the body which is produced by the pancreas.
- Understanding normal blood sugar levels is important because it can help you monitor and manage your overall health. Here are some key points:
1. Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS): This is the blood sugar level measured after an overnight fast, usually 8 hours without eating. A normal fasting blood sugar level is typically considered to be between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or 3.9 to 5.6 millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
2. Postprandial Blood Sugar (PPBS): This is the blood sugar level measured a couple of hours after eating a meal. A normal postprandial blood sugar level is usually below 140 mg/dL or 7.8 mmol/L.
3. HbA1c (Glycated Hemoglobin): HbA1c reflects your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It provides an indication of how well your blood sugar has been controlled over time. A normal HbA1c level is approximately less than 5.7%.
4. Implications of High Blood Sugar: Elevated blood sugar levels over time can lead to various health complications, especially in individuals with diabetes. Long-term high blood sugar can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
5. Factors Affecting Blood Sugar: Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, illness, medications, and genetics. Monitoring and managing these factors can help maintain normal blood sugar levels.
It’s important to note that individual variations exist, and what’s considered normal can vary from person to person. If you have concerns about your blood sugar levels, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and recommendations.