Recognizing the Symptoms of Diabetes in Women: A Comprehensive Guide.
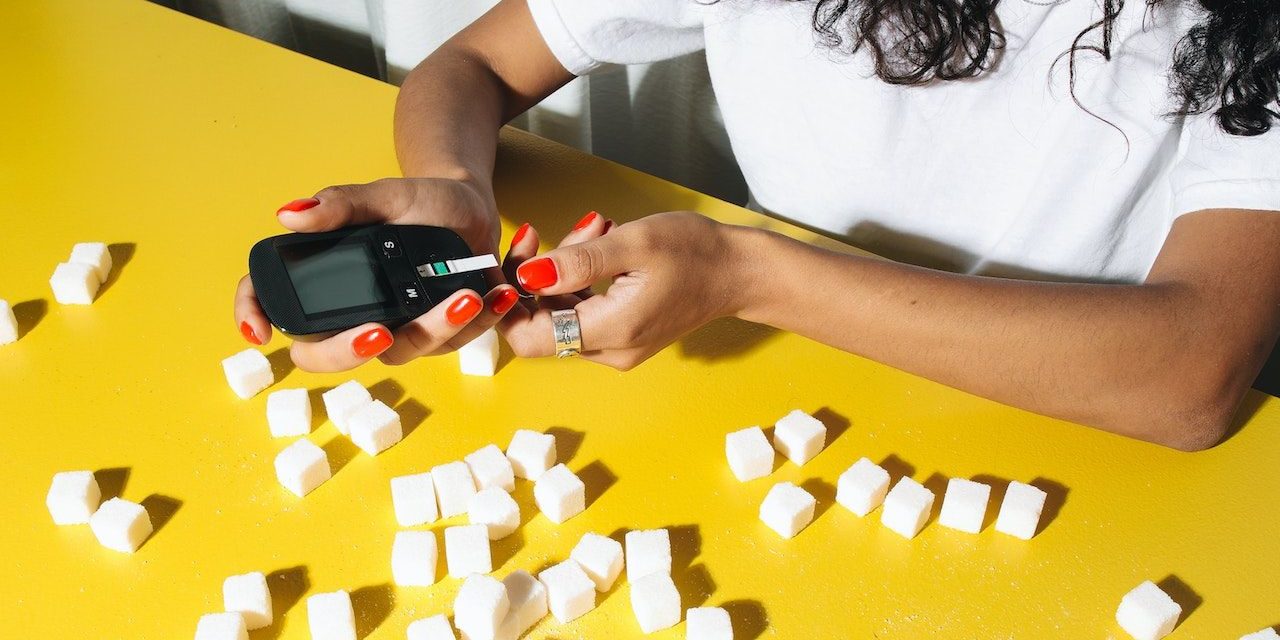
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that affects how the body uses glucose (sugar) for energy. Although the symptoms of diabetes can be the same in both men and women, there are some aspects that are particularly relevant to women. Here is a comprehensive guide to spotting the symptoms of diabetes in women:
1. Abnormal thirst and frequent urination:
Excessive thirst (polydipsia) and increased urination (polyuria) are common symptoms of diabetes. Women with diabetes may have increased frequency and volume of urination, often waking up at night to urinate (nocturia). This happens because high blood sugar causes the kidneys to work harder to filter and absorb excess glucose.
2. Fatigue and weakness:
Constant fatigue and weakness are common symptoms of diabetes. Women with diabetes may feel tired even after plenty of rest, because the body’s cells are not using glucose efficiently for energy due to insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production.
3. Unexplained weight changes:
Significant weight loss or weight gain for no apparent reason can be a sign of diabetes in women. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to weight loss as the body breaks down muscle and fat for energy. On the other hand, some women may experience weight gain due to insulin resistance, especially in the abdominal area.
4. Frequent infections
Women with diabetes may be more prone to infections, especially in the urinary tract, bladder and vagina. High blood sugar levels create a favorable environment for bacteria and yeast to grow. Symptoms may include urinary tract infections, vaginal yeast infections, and slow-healing skin infections.
5. Changes in Menstrual Cycle:
Fluctuations in blood sugar levels can affect hormone balance and disrupt menstrual cycles in women with diabetes. Some women may experience irregular periods, longer or heavier periods, or even a complete absence of periods.
6. Yeast infections:
High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of yeast infections, such as vaginal candidiasis. Women with diabetes may experience persistent itching, burning, or abnormal discharge in the genital area. These infections may be more frequent and more difficult to treat in women with poorly controlled diabetes.
7. Sexual impotence:
Diabetes can affect sexual health in women. This can lead to decreased libido, vaginal dryness, and difficulty achieving orgasm. These symptoms can be caused by nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy), decreased blood flow, or hormonal imbalances associated with diabetes.
8. Vision problems:
Diabetes can affect the eyes and lead to various vision problems. In women, diabetic retinopathy, a condition characterized by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, can cause blurred vision, floaters, or even loss of vision if left untreated.
9. Gestational Diabetes:
During pregnancy, some women develop a temporary form of diabetes known as gestational diabetes. It usually occurs in the second or third trimester and resolves after childbirth. Women with gestational diabetes may experience symptoms similar to type 2 diabetes, such as increased thirst, frequent urination and fatigue.
It is important to note that the presence of these symptoms does not mean that a woman has diabetes. However, if you are experiencing any of these symptoms or have concerns about your health, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis, evaluation and management.